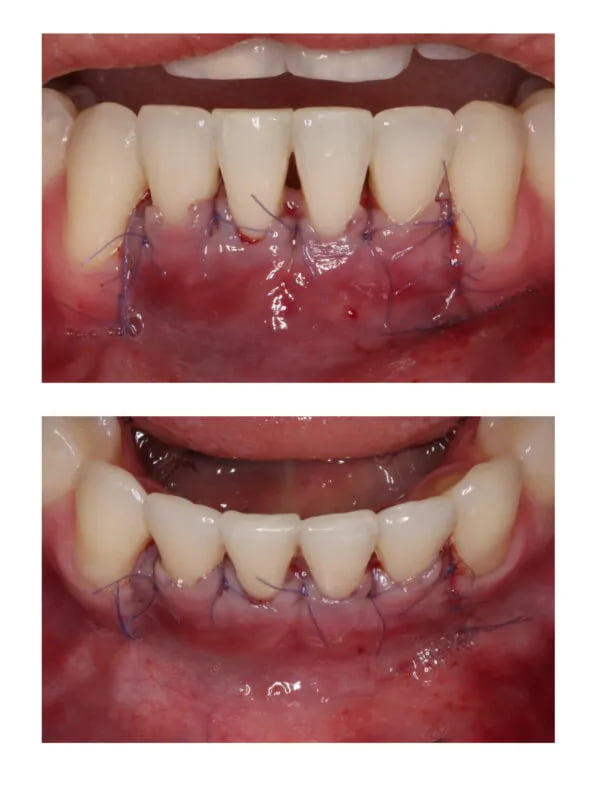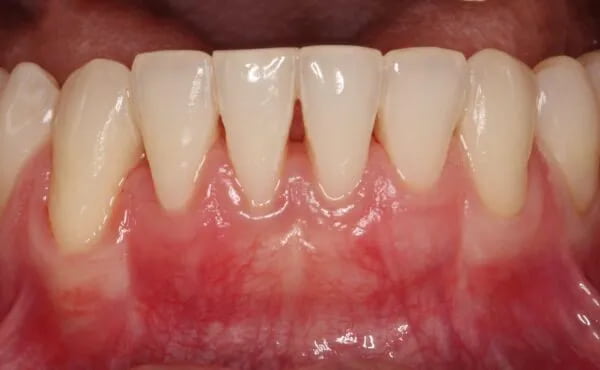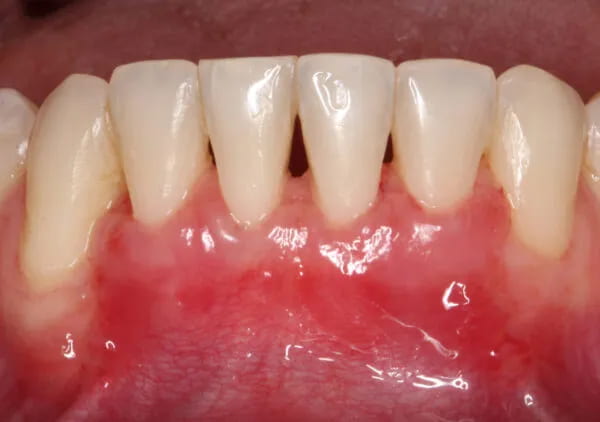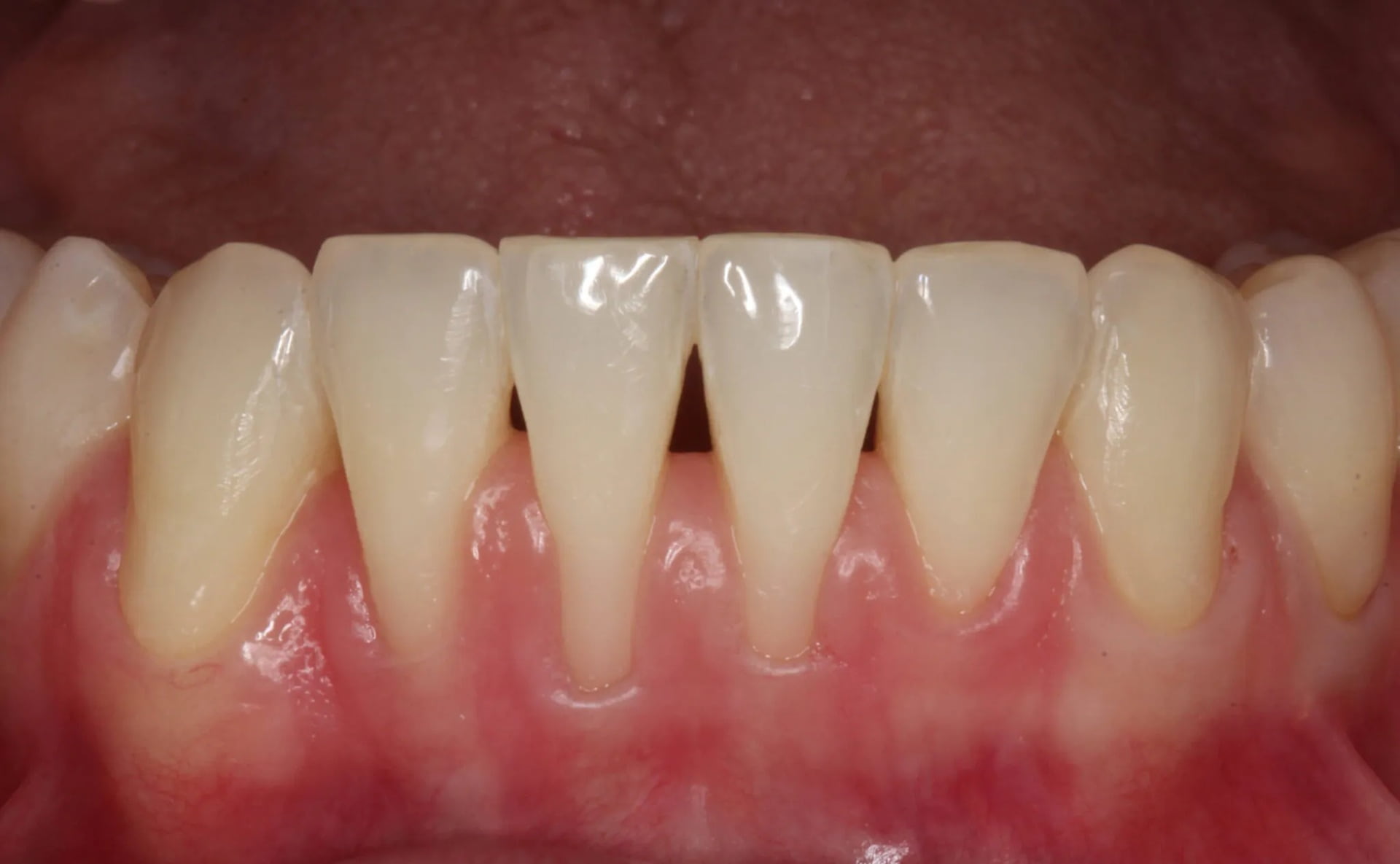
Clinical Case Study 4 - Multiple gingival recession coverage at lower incisors using the vertically coronally advanced flap technique with a subepithelial connective tissue graft
20th of December 2022
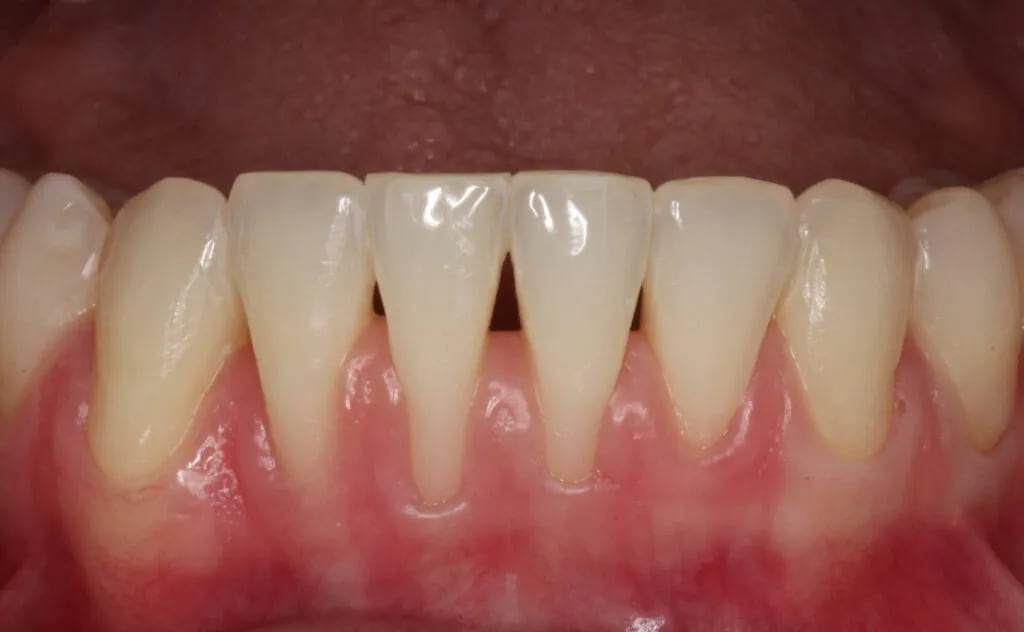
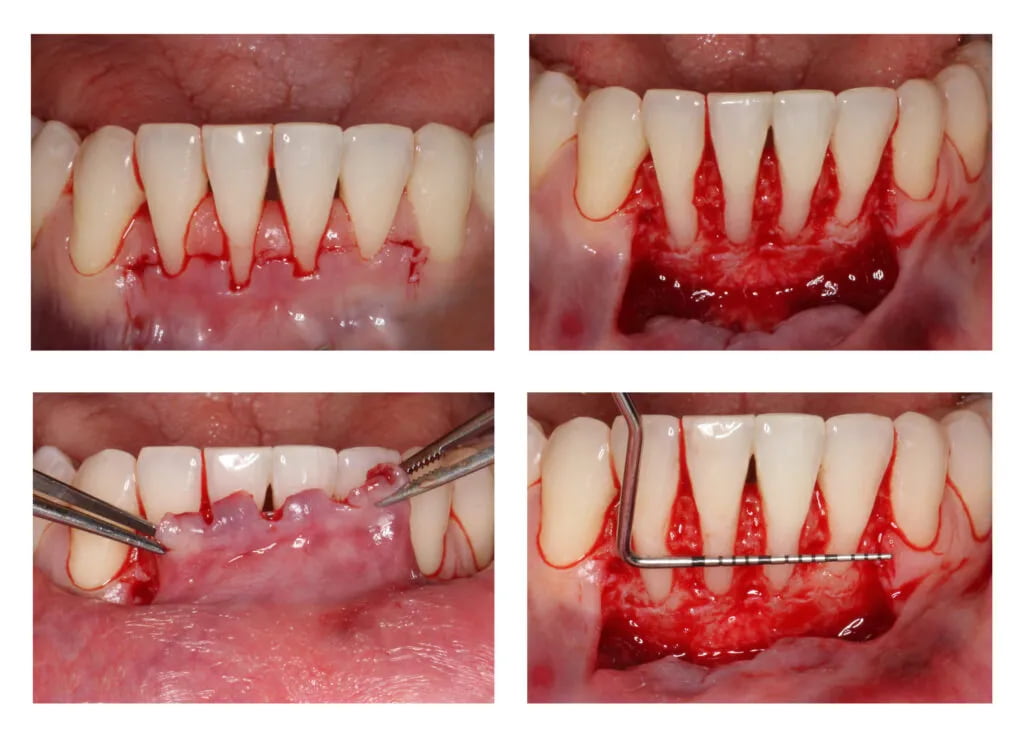
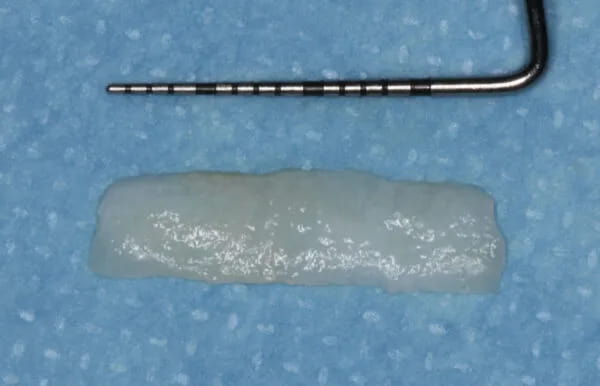
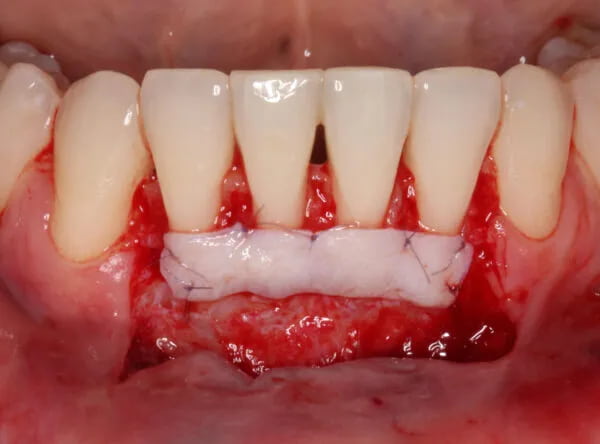
Recessions at lower incisors frequently co-exist with thin gingival phenotype, a very narrow zone of keratinized tissue, and shallow vestibule, therefore, surgical procedures ought to account for all of the above-mentioned factors. The vertically coronally advanced flap prepared from lower labial mucosa is dedicated to this particular clinical scenario. In this technique, the flap is prepared in a split-full-split manner. From the periosteal surface located apically to the dehiscence of the bone, the submucosal tissue is removed together with the muscle attachments, thus creating a bed for the subepithelial connective tissue graft. The exposed tooth root surfaces are prepared mechanically and chemically with 24% EDTA and enamel matrix derivatives. The subepithelial connective tissue graft was then positioned at the level of the cementoenamel junction of all the incisors. Verticalization of the surgical flap was achieved using periosteal sutures, positioned in the apical parts of the vertical incisions. A coronally advanced flap should cover the entire connective tissue graft. Sutures were removed after fourteen days. The vertically coronally advanced flap technique produces optimal esthetic effects, and restores the optimal vestibule depth, thus facilitating home plaque control (the final photo was taken after four weeks).